VMware Overview
VMware is a leading American software company specializing in virtualization technology and cloud computing services. Its suite of products enables organizations to optimize their IT infrastructure by efficiently managing and deploying virtual machines (VMs) across various environments.
Hypervisors by VMware
VMware offers two primary hypervisors:
- ESXi – A Type 1 hypervisor that runs directly on bare metal hardware, providing a robust platform for creating and managing multiple virtual machines without requiring an underlying operating system.
- Workstation Pro – A Type 2 hypervisor that operates on top of an existing operating system (such as Windows, macOS, or Linux), allowing users to create and manage VMs within the host OS environment.
Understanding Hypervisors
Hypervisors are software layers that enable the creation, management, and operation of virtual machines (VMs). They come in two types:
- Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare-Metal):
A Type 1 hypervisor, like VMware’s ESXi, installs directly on the physical hardware, bypassing the need for a host operating system. This setup is ideal for enterprise environments, providing high performance and direct access to the hardware’s resources. ESXi is a prominent example, enabling the creation of multiple VMs on a single server, optimizing resource utilization. - Type 2 Hypervisor (Hosted):
A Type 2 hypervisor, such as VMware’s Workstation Pro, runs atop a host operating system. It utilizes the host OS’s services, including I/O management, memory allocation, and device support, to manage VMs. This type of hypervisor is often used in desktop environments where users require flexibility in running different OS instances on their personal computers.
VMware’s Key Products
ESXi
ESXi is VMware’s Type 1 hypervisor, designed to be installed directly on physical servers. By doing so, it allows the server’s resources to be fully utilized by creating and running multiple virtual machines. This capability is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of hardware investments in data centers.
vSphere
vSphere is a comprehensive management interface that simplifies the administration of VMs hosted on ESXi servers. Users access vSphere through a web browser by connecting to the ESXi host’s IP address. However, vSphere manages only one ESXi host at a time.
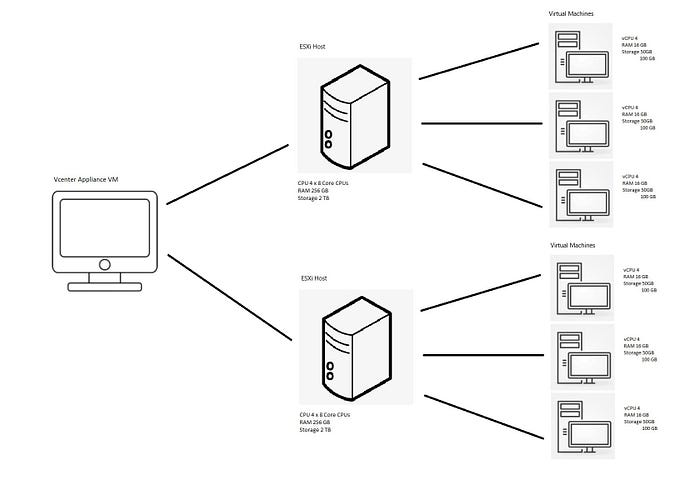
vCenter
vCenter extends the functionality of vSphere by providing centralized management of multiple ESXi hosts and their respective VMs. It offers advanced features such as:
- vMotion: Facilitates the live migration of VMs between ESXi hosts with no downtime.
- VM Cloning: Creates exact replicas of existing VMs, useful for testing and scaling.
- High Availability (HA): Automatically restarts VMs on other hosts if a failure occurs, minimizing downtime.
- Fault Tolerance (FT): Ensures continuous operation by running a shadow VM that takes over instantly if the primary VM fails.
- Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS): Optimizes resource usage across ESXi hosts in a cluster by dynamically balancing VM workloads.
Workstation Pro
Workstation Pro is VMware’s Type 2 hypervisor, ideal for desktop virtualization. It allows users to run multiple VMs on a single personal computer. The host operating system manages the resources necessary for these VMs, making it a powerful tool for developers, testers, and IT professionals.
Example: ESXi Host and VM Utilization
Consider a high-capacity server with abundant resources. By installing ESXi directly on this server, you can create several VMs, each utilizing portions of the server’s resources. This approach ensures that the server’s capabilities are fully leveraged. Each VM is accessible via its unique IP address through a web browser, using vSphere for management. For broader management needs, vCenter provides a unified platform to control and monitor all VMs and ESXi hosts in the infrastructure.
